Profit is the ultimate goal of any business. It is the financial gain that results from the difference between the amount earned and the amount spent in buying, operating, or producing something. Understanding profit is crucial for anyone involved in business, from entrepreneurs and managers to investors and analysts. This guide delves into the key components of profit, the metrics used to measure profitability, and strategies to enhance it.
Key Components of Profit
Profit can be broken down into several key components, each representing different aspects of a company’s financial performance.
1. Gross Margin
Gross margin is the difference between sales and the cost of goods sold (COGS). It represents the core profitability of a company’s products or services before accounting for operating expenses.
Formula: Gross Margin=Sales−COGS
2. Operating Income
Operating income, also known as operating profit, is the profit realized from a company’s core business operations. It is calculated by deducting operating expenses from the gross margin.
Components of Operating Expenses:
Sales and Marketing
Administration
Research and Development (R&D)
Depreciation
Formula: Operating Income=Gross Margin−Operating Expenses
3. Non-Operating Income
Non-operating income includes revenues and expenses not related to the core business operations. This can include interest income, other miscellaneous income, interest expenses, and taxes.
Components of Non-Operating Income:
Interest Income
Other Income
Interest Expense
Taxes
4. Net Income
Net income, also known as net profit or the bottom line, is the total profit of a company after all expenses have been deducted from total revenues. It includes both operating and non-operating income and expenses.
Formula: Net Income=Operating Income+Non-Operating Income
Key Profitability Metrics
To effectively measure and manage profitability, businesses use several key performance indicators (KPIs). Here are the top three profitability KPIs:
1. Gross Margin Ratio
The gross margin ratio indicates how efficiently a company is producing its goods or services relative to its sales. A higher ratio suggests better efficiency and profitability.
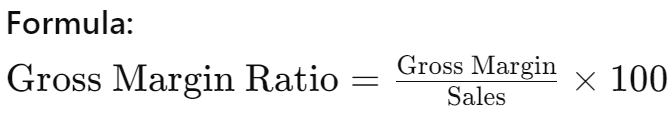
2. Net Income Margin
The net income margin measures the percentage of revenue that remains as profit after all expenses are paid. It reflects the overall profitability and financial health of a company.
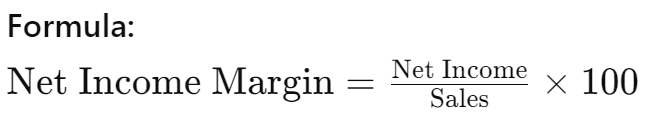
3. Return on Equity (ROE)
Return on equity measures the profitability of a company in generating profit from its shareholders’ equity. It indicates how effectively the management is using the equity invested by shareholders to generate earnings.

Strategies to Enhance Profitability
Enhancing profitability involves increasing revenues, reducing costs, or a combination of both. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Increase Sales
a. Expand Market Reach
Target new customer segments or geographic markets to increase sales volume.
b. Improve Product Offerings
Enhance product features, quality, or introduce new products to attract more customers.
c. Enhance Marketing Efforts
Invest in marketing campaigns to boost brand awareness and drive sales.
2. Optimize Pricing
a. Value-Based Pricing
Set prices based on the perceived value to the customer rather than just cost-plus pricing.
b. Dynamic Pricing
Adjust prices based on demand, competition, and other market factors in real-time.
3. Reduce Costs
a. Streamline Operations
Identify and eliminate inefficiencies in the production or delivery processes.
b. Negotiate with Suppliers
Seek better terms or bulk discounts from suppliers to reduce COGS.
c. Automate Processes
Invest in technology to automate repetitive tasks, reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency.
4. Improve Cash Flow Management
a. Efficient Inventory Management
Maintain optimal inventory levels to reduce holding costs and avoid stockouts.
b. Manage Receivables
Implement strict credit policies and follow up on overdue accounts to ensure timely collections.
c. Control Expenses
Regularly review and control operating expenses to avoid unnecessary spending.
5. Leverage Technology
a. Data Analytics
Use data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency.
b. E-commerce Platforms
Expand online presence through e-commerce platforms to reach a broader audience.
c. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Implement CRM systems to enhance customer service and loyalty, leading to repeat business.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
1. Ignoring Market Trends
Failing to keep up with market trends and customer preferences can lead to declining sales and profitability. Regular market research and customer feedback are crucial.
2. Overexpansion
Expanding too quickly without adequate planning and resources can strain finances and operations, leading to inefficiencies and losses.
3. Poor Financial Management
Neglecting financial management, such as cash flow monitoring and expense control, can jeopardize a company’s profitability and sustainability.
4. Inadequate Cost Control
Failing to control costs effectively can erode profit margins. Regularly review and optimize cost structures to maintain profitability.
5. Lack of Diversification
Relying heavily on a single product or market can be risky. Diversifying product offerings and markets can spread risk and enhance profitability.
Case Study: Successful Profit Enhancement
Company XYZ
Company XYZ, a mid-sized manufacturing firm, faced declining profits due to rising production costs and stagnant sales. By implementing the following strategies, the company successfully turned around its profitability:
Strategies Implemented:
Market Expansion
Targeted new geographic markets, increasing sales by 20%.
Product Improvement
Enhanced product features and quality, leading to higher customer satisfaction and repeat business.
Cost Optimization
Streamlined production processes, reducing waste and lowering production costs by 15%.
Dynamic Pricing
Implemented dynamic pricing strategies, optimizing prices based on demand and competition.
Cash Flow Management
Improved inventory management and receivables collection, enhancing cash flow and reducing holding costs.
Results:
Gross Margin: Increased from 30% to 35%.
Net Income Margin: Improved from 8% to 12%.
Return on Equity: Rose from 10% to 15%.
Company XYZ’s success demonstrates the effectiveness of a comprehensive approach to enhancing profitability through strategic planning and execution.
Conclusion: Understanding Profit: A Comprehensive Guide to Profitability
Understanding and managing profit is essential for the success and sustainability of any business. By focusing on key profitability metrics, implementing effective strategies, and avoiding common pitfalls, businesses can enhance their profitability and achieve long-term growth. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, manager, or investor, a thorough understanding of profit dynamics is crucial for making informed decisions and driving financial success.

















