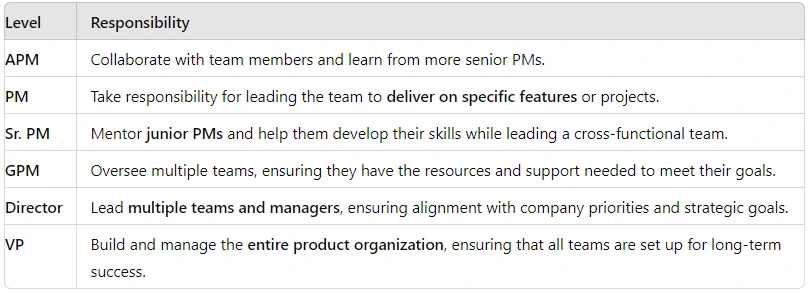
Product manager competencies is a complex and rewarding field that requires a wide range of skills and competencies. Whether you’re an Associate Product Manager (APM) just starting out, or a Vice President of Product (VP) leading a large team, understanding the key competencies that define success at every level is essential.
In this detailed guide, we’ll break down the competencies that every Product Manager (PM) should master, organized into four key areas:
Product Execution: Define, build, and launch exceptional products.
Customer Insight: Understand and fulfill customer needs.
Product Strategy: Deliver business impact via product innovation.
Influencing People: Rally your team and stakeholders to achieve goals.
These competencies evolve as you grow in your career, from Associate PM to VP of Product. Let’s dive into the details of each competency and explore how you can master product management at every level! 🎯
1. Product Execution: Define, Build, and Launch Exceptional Products
Product execution is the backbone of product management. It involves gathering requirements, defining product features, working closely with the development team, and ensuring high-quality delivery. As you progress in your career, the scope of your product execution responsibilities expands.
Feature Specification 📝
At every level, the ability to gather requirements, define functionality, and set goals is crucial. Product Managers must provide a clear, actionable format that can be communicated to the team.

💡 Tip: As you progress, it becomes important to ensure that feature specifications align with the broader company strategy. This requires developing a strategic mindset.
Product Delivery
Delivering the product is more than just managing timelines. It involves working closely with engineering, design, and other teams to ensure that features are built according to the specification and delivered on time.

Practical Example: Imagine you’re an APM working on a new mobile app feature. You’ll need to work closely with the design team to get mockups, collaborate with developers to ensure the feature is built according to spec, and perform user testing to ensure the feature works seamlessly.
Product Quality Assurance
Delivering a product that meets the required quality standards is essential. Product Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on ensuring the product is functional, meets user needs, and aligns with business goals.

💡 Tip: As a PM progresses, product quality becomes less about identifying individual bugs and more about ensuring processes and standards are in place to guarantee quality across the organization.
2. Customer Insight: Understand and Fulfill Customer Needs
A successful product manager must deeply understand the needs of their customers. This means gathering data, listening to customer feedback, and ensuring that user experience is a top priority.
Fluency with Data
Product Managers need to be data-driven. This involves using data to guide decisions, validate hypotheses, and measure success.

Practical Example: As a PM, you might use conversion rate data from a product feature to decide whether to iterate on the current feature or pivot to a new solution. Being fluent with data helps you justify your decisions with real insights rather than gut feelings.
Voice of the Customer
Understanding the Voice of the Customer (VoC) is critical for building products that meet real user needs. Product managers must gather feedback from customers and translate that into actionable insights.

Tip: As you grow in your product career, it’s crucial to develop processes for listening to customer feedback at scale, ensuring that the Voice of the Customer is heard throughout the organization.
User Experience Design (UX)
UX design focuses on creating products that are not only functional but also intuitive and easy to use. Understanding the principles of UX is crucial for every PM, as it directly impacts customer satisfaction.

Practical Example: As a PM, you might lead an initiative to improve the onboarding flow for a new app. By working closely with UX designers and conducting usability tests, you ensure that new users have a seamless experience, which improves retention rates.
3. Product Strategy: Deliver Business Impact via Product Innovation
Product strategy is where vision meets execution. It’s about setting the direction for your product and ensuring that your team delivers business impact. As you progress in your PM career, your role in shaping product strategy will grow in scope and complexity.
Business Outcome Ownership
Product Managers must own the business outcomes related to their product. This means tying product functionality to measurable business goals.
💡 Tip: As you move into more senior roles, it’s important to focus on the business impact of your product decisions. This means making sure that every feature contributes to the company’s strategic goals.

Product Vision & Roadmapping
Setting a clear product vision and defining the roadmap to achieve that vision is one of the most important roles of a PM. This skill grows in importance as you move into senior PM roles.

Practical Example: As a GPM, you might oversee the development of a new product line. You’ll define the high-level vision, set clear goals, and create a roadmap that guides teams from initial concept to market launch.
Strategic Impact
The ability to contribute to company strategy is a defining skill for senior PMs. At higher levels, Product Managers need to ensure that their product decisions drive business strategy and move the company forward.

💡 Tip: Developing strategic thinking is crucial as you rise in the PM ranks. Understand how your product decisions affect the company’s position in the market and drive growth.
4. Influencing People: Rally Your Team and Stakeholders
Product Managers don’t just manage products—they manage people. From team leadership to stakeholder management, the ability to influence others is crucial for ensuring that everyone is aligned and working toward common goals.
Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management is about identifying the key players impacted by your product and ensuring that their needs are considered in product decisions.

Practical Example: As a Sr. PM, you might work with marketing, sales, and customer support teams to ensure that all feedback is considered when planning new features. This ensures alignment across departments and improves cross-functional collaboration.
Team Leadership
As you grow in your career, leadership becomes a key competency. Great PMs inspire and guide their teams toward success, helping each team member grow and achieve their goals.
💡 Tip: Great leadership is about more than just giving directions—it’s about mentoring, empowering others, and ensuring that every member of the team can succeed.
Conclusion: Mastering Product Manager Competencies at Every Level
Mastering the competencies of a Product Manager is a journey that evolves as you progress through your career. Whether you’re an APM just starting out or a VP overseeing a large organization, the core competencies remain the same: product execution, customer insight, product strategy, and influencing people.
By focusing on these key areas and continuously developing your skills, you can grow into a highly effective product leader. With each level comes new challenges, but also the opportunity to drive greater impact for your company, your customers, and your team. 🎯
Now that you’ve explored these competencies in detail, it’s time to put them into practice. Whether you’re defining a new feature, creating a product roadmap, or mentoring your team, remember that great product managers never stop learning. Keep honing your skills, and you’ll be well on your way to mastery.